Key Takeaways:
- Strong preregistration and registration drive faster payments.
- Missed charges and write-offs often stem from weak processes.
- Claim scrubbing and automation reduce errors—but require oversight.
- Clear payment policies boost patient collections.
- Regular audits improve cash flow and reduce risk.
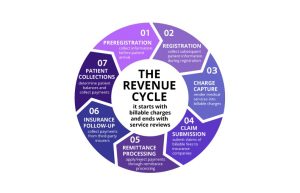
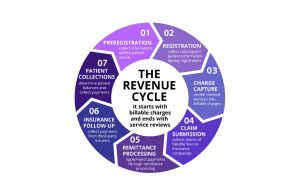
The seven steps of revenue cycle include preregistration, registration, charge capture, claim submission, remittance processing, insurance follow-up and patient collections. This article reviews each of these steps, what’s entailed in them, what can go wrong within the revenue cycle process, and how to prevent missteps.
What is Revenue Cycle Management in Healthcare?
Revenue cycle management (RCM) is the process used by healthcare systems in the United States to track revenue from patients from their initial appointment or encounter with the healthcare system to their payment of balance. Revenue cycle starts with the appointment or hospital visit and ends when the provider or hospital gets paid fully for the services provided.
RCM is not just billing; it supports a healthcare organization’s financial sustainability, meeting regulatory requirements, and enhancing the patient experience. This process impacts nearly every department and function.
What makes RCM so important right now?
- New payment models, such as value-based care, require a closer connection between clinical outcomes and financial operations.
- Interoperability requirements and AI tools are changing the way data moves throughout the revenue cycle.
- Using analytics and automation can significantly cut down on manual errors, accelerate reimbursements, and help spot financial risks more quickly.
- The National Institutes of Health estimates that inefficiencies in RCM cost U.S. healthcare providers around $262 billion each year. Healthcare leaders should take this as a clear signal to invest in smarter and more agile RCM strategies.
Benefits of Revenue Cycle Management in Healthcare
A strong revenue cycle doesn’t just keep the lights on, it helps your whole practice run better. When the financial side of healthcare works the way it should, everything else tends to follow. Patients get fewer billing surprises. Staff can focus on care instead of chasing paperwork. And providers can grow with more confidence.
Today’s leading practices are using smarter tools — like AI-driven coding, automated claims workflows, and real-time denial analytics — to simplify what used to be manual and messy. As value-based care and interoperability evolve, the right RCM approach helps you stay ahead of change.
Here’s what efficient revenue cycle management can do:
- Make patients happier. Transparent billing and fewer delays help patients feel more confident about their care.
- Improve cash flow. Clean claims and accurate charge capture mean faster payments and fewer missed dollars.
- Reduce denials and rework. With smarter tools in place, you can catch issues before they become problems.
- Support compliance. A clean process with the right controls reduces audit headaches and helps you stay aligned with payers.
- Create room to grow. When systems run smoothly, your team can focus on what’s next — not just keeping up.
- Free up clinical staff. When billing works, providers can spend less time on paperwork and more time with patients.
At the end of the day, better RCM means better outcomes — for your finances, your team, and the people you care for.
Webinar: Revenue Cycle of the Healthcare Practice 101
Kathi reviews the revenue cycle of healthcare practices, processes that need to be in place, and how to analyze your existing process and auditing processes.
On-Demand Webinar Duration: 49:56
Speaker: Kathi Rennick, CPC, CPMA, CPC-I, CHC, Director, LBMC Physician Business Solutions, LLC
Recorded February 9, 2021
7 Steps of Revenue Cycle Management in Healthcare
Below is a refreshed overview of each revenue cycle step with updated strategies to reflect today’s reality, including automation, payer complexity, and analytics tools.
| Revenue Cycle Step | Purpose | Revenue Cycle Optimization Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Preregistration | Collect patient info, verify insurance, and confirm coverage before appointments. | Use clearinghouse integrations for real-time eligibility checks, digital intake forms for accuracy, and scripts for staff to set payment expectations early. |
| 2. Registration | Confirm demographic and insurance information, collect copayments, and obtain necessary authorizations. | Automate verification workflows, require e-signatures on financial documents, and track registration accuracy with audit trails. |
| 3. Charge Capture | Document and transfer all billable services accurately. | Use EHR-integrated coding tools, automate charge entry, and audit ancillary service coding regularly. |
| 4. Claim Submission | Submit clean, accurate claims to payers for reimbursement. | Deploy AI-driven claim scrubbing, track rejections in real time, and automate claims routing via clearinghouses. |
| 5. Remittance Processing | Review payments, adjustments, and denials from payers. | Automate remittance posting, flag anomalies with analytics, and perform regular denial and write-off reviews. |
| 6. Insurance Follow-Up | Resolve unpaid or underpaid claims and monitor AR. | Use denial analytics to prioritize follow-up, assign payers by team expertise, and automate claim status tracking. |
| 7. Patient Collections | Secure payment from patients for their share of the cost. | Offer online payment options, automate daily statements, and use text/email reminders to encourage prompt payment. |
Each step in the revenue cycle now benefits from smarter tools, real-time data, and patient-centric workflows. Practices that modernize each phase are better positioned to improve cash flow, reduce denials, and support overall growth.
1. Preregistration
Preregistration is the first and most vital step in the revenue cycle process. Preregistration allows the medical practice to capture demographic information, insurance information and eligibility in real-time through a clearinghouse, often while the patient is still on the phone. Information goes to the patient’s insurance carrier and flows through the provider’s practice management system, then tells the provider the patient’s coverage, deductible, co-insurance, co-payment, and in certain instances, if a referral is needed. Many practices now integrate digital intake platforms to reduce manual entry errors and accelerate insurance validation.
During preregistration, the practice can discuss financial expectations of the patient, including time of payment and no-show/cancellation policy. The preregistration process allows a practice to set the financial tone at the beginning and prevents questions about payment. Clear communication at this stage reduces the risk of downstream collection issues. If a practice doesn’t have a tight preregistration process, there are many areas that can get missed. Check your preregistration process to get your revenue cycle process off to a strong start.
2. Registration
Registration solidifies the process of ensuring the patient’s information is 100% accurate from start to finish. During registration, the provider makes sure the patient’s address, phone number, date of birth, guarantors, and insurance information are correct, and it’s critical they secure this data each time a patient is treated. Many organizations now use electronic signature capture and ID scanning to automate and verify these details.
During registration, the provider collects co-payments, and if it’s a specialist, they will ensure a referral or authorization is in place to treat the patient. If that step is missed in a specialist’s office, it is unlikely they will get paid for that service in the end. During registration, financial forms are signed, and insurance benefits are assigned. In the event these steps are missed and the practice is audited, there’s the risk of financial repercussion. Integrated financial clearance tools can assist staff in tracking required documents and real-time authorization status.
If you are unsure about your registration process, consult an expert to review it. Making sure step two in the revenue cycle process is clean and thorough will save you headaches in the long run.
3. Charge Capture
Charge capture, step three in the revenue cycle process, can be done a couple of different ways. It can be automated, where the information automatically flows into the practice management billing side based on what the provider puts in their documentation. The other option is the old-fashioned way, where front desk staff enter information or send it to billing, where it’s manually keyed in. AI-assisted coding is emerging as a tool to flag incomplete or inconsistent documentation before charges are missed.
There are advantages and disadvantages to both approaches, as there are charges that can be missed either way. One commonly missed charge includes ancillary services, which results in revenue left on the table. To prevent missing charges, make sure you are coding charges and getting them to the insurance carrier correctly. Regular charge reconciliation audits and EHR-integrated coding dashboards can improve capture accuracy.
If you are concerned that you may not be accounting for all charges, consult an expert to review your charge capture process. As part of a revenue cycle audit, an experienced advisor can follow a charge from start to finish, uncover missing charges, and identify miscoded charges. Making sure you are capturing your charges correctly is an important piece of the revenue cycle process.
4. Claim Submission
Claim submission includes sending information to the insurance carrier after the charges have been entered. The revenue cycle team will look at the charges, the CPT code, and the diagnosis code. They will ask whether the diagnosis will support the procedure performed. If two services are provided, those need to be separated and coded correctly.
Claim scrubbing is the process of making sure claims are clean and going in the door correctly. If a claim gets to the insurance carrier clean, it will get paid a lot faster. The process includes sending the claims from your practice management system to a clearinghouse, which acts as a mailroom, taking in the claims and sending them to the different payers. AI and predictive analytics tools now help scrub claims for accuracy and prioritize high-value rejections.
The transmission report shows claims sent, claims coming back in, and claims dropped, while the rejections report identifies incorrect codes. Make sure you review both reports as part of the claim submission process. The sooner errors are identified, the sooner they can be fixed, and the sooner the claims will get paid. Automating report monitoring helps billing teams respond faster to prevent revenue leakage.
If you have questions about the claim submission process, consult an expert to help you sort it out. It’s better to have clear answers on the front end than wait until it is too late to correct a problem.
5. Remittance Processing
Step five in the revenue cycle is remittance processing. Once a practice’s claims have gone out, they will get remittances back. The explanation of benefits shows the practice what they got paid for the services provided. During this process, allowables are determined. Allowables are what the provider has contracted with the insurance carrier on a service provided. The provider and carrier negotiate the contract, at which time the insurance company will confirm how much they will pay for each service.
One common mistake during the remittance process is “post and go.” As electronic posting has become the norm for the revenue cycle, a practice can encounter problems when they post remittances and never look at them again. For example, if a carrier does not pay or something is set up incorrectly in the practice management system, the error could get missed in the “post and go” scenario. If no one is reviewing the process or the reports, a practice could miss the chance for an appeal and thus an opportunity to correct a mistake. Advanced reporting and flagging systems now alert teams to payment anomalies in real time.
Another element of remittances are fee schedules, which are the amounts providers charge for each of their services. Providers should review their fee schedules on an annual basis to make sure they are in line with adjusting rates, contracts, and allowables. Evaluate your fees regularly to make sure you are not leaving money on the table.
The final piece of the remittance process includes write-offs, both contractual and non-contractual. Contractual write-offs are unpreventable, as they involve contracted rates with carriers and payers.
On the other hand, non-contractual write-offs are avoidable; they include write-offs that would have not happened with a tight process in place, either at the beginning, the end, or somewhere along the way. Avoidable write-offs are generally the result of a breakdown in the provider’s remittance process and can be prevented by looking at reports. Red flags include no authorization, no referral on file, and claim not submitted in a timely manner.
There are multiple points in the remittance process that can affect your revenue cycle. If you are unsure about your remittance process, consult an expert to do a deep dive.
6. Insurance Follow-up
The next step in the revenue cycle process is insurance follow-up. In this stage, practices look at not only what has been paid, but also what has not been paid. What happens to the items that don’t get paid?
The accounts receivable (A/R) report shows everything that’s sitting in the insurance and/or patient buckets for a period of time. This report will show if insurance follow-up is broken and why it is taking so long to get it paid. Denial management tools and payer-specific analytics help identify root causes and speed resolution.
An important piece of insurance follow-up is determining the structure. Questions to ask include:
- Are people assigned certain carriers?
- Is your billing team cross-trained?
- Do you have more than one billing person who can work on Medicare?
- Is the practice management team working this insurance?
- Are you seeing any noticeable changes on the aging monthly?
- Are claims being appealed or are they being resubmitted?
Today’s most efficient teams assign payer reps by expertise and use queue management tools to track follow-up status and cycle times. If you are concerned your insurance follow-up piece is broken, bring in a consultant to advise you on how to fix it.
7. Patient Collections
The most difficult part of the revenue cycle process is patient collections. The best time to get money from a patient is when they are in your office. For that reason, it’s recommended that front desk staff are trained to collect at the time of service. To prevent the collections backlog from snowballing, make sure you have a standard policy for collecting copayments and deductibles that sets the financial expectations for the practice. Digital payment tools and text reminders now help patients pay faster and more conveniently.
Just as important is making sure routine patient statements go out. The best practice is a daily statement cycle – your patients will get one statement every 30 days, but statements to go out more quickly, allowing you to get your revenue cycle moving better and your cash flow gets accelerated. Mobile billing platforms and self-service portals are becoming must-haves for collection success.
Revenue Cycle Management Services from LBMC
When revenue cycle processes break down, it’s not just your cash flow that suffers — it affects your staff, your patients, and your peace of mind. Whether you’re facing delays, denials, or growing A/R, now is the time to take a closer look. You don’t have to do it alone.
LBMC’s Healthcare Advisory team works closely with healthcare organizations to improve operational efficiency, reduce claim denials, and strengthen cash flow. We help you identify what’s working, what needs fixing, and how to build a revenue cycle that truly supports your mission.
We serve clients from offices in Chattanooga, Memphis, Louisville, Nashville, Knoxville, and Charlotte, and we also provide online consulting support for practices nationwide.
Ready to tighten up your processes and get paid faster? Explore our revenue cycle management services and see how LBMC can help.
Content provided by Kathi Rennick, Executive Director and Partner at LBMC Physician Solutions, LLC.
Webinar: RCM and AI in Action
Curious how generative AI is transforming revenue cycle management? Hear real-world examples and expert insights in our on-demand webinar or reach out to LBMC for a deeper dive.
FAQs about Revenue Cycle Management in Healthcare
What is the process of revenue cycle management in healthcare?
Revenue cycle management (RCM) is the full journey from patient scheduling to payment. It includes seven key steps: preregistration, registration, charge capture, claim submission, remittance processing, insurance follow-up, and patient collections. Each step plays a role in getting providers paid accurately and on time.
What’s the difference between revenue cycle management and medical billing?
Medical billing is just one part of the revenue cycle — it’s mostly focused on submitting claims and posting payments. RCM is a broader, strategic process that ties together front-desk operations, clinical documentation, billing, collections, and financial reporting.
What are the biggest challenges in revenue cycle management for healthcare organizations?
Common pain points include denied claims, delays in insurance follow-up, inaccurate charge capture, and slow patient collections. Many organizations also struggle with outdated systems, staffing shortages, and keeping up with payer rule changes.
What KPIs should healthcare organizations track in revenue cycle management?
Start with these: days in A/R, denial rate, clean claim rate, net collection rate, and patient collection rate at time of service. Tracking these regularly helps you spot bottlenecks and measure improvements.
How can automation and AI improve revenue cycle management in healthcare?
Automation reduces manual errors and frees up staff time. AI can flag coding issues, predict denials, and prioritize claims for follow-up. Together, they help you get paid faster, more accurately, and with less stress.
What services does LBMC offer for healthcare revenue cycle management?
LBMC provides customized RCM support — from process reviews and denial management to charge capture audits and performance coaching. We help healthcare providers strengthen their financial operations so they can focus more on patient care.